|
Type |
Topic |
# |
Climate-related risk |
Relevance to Heijmans |
|
|
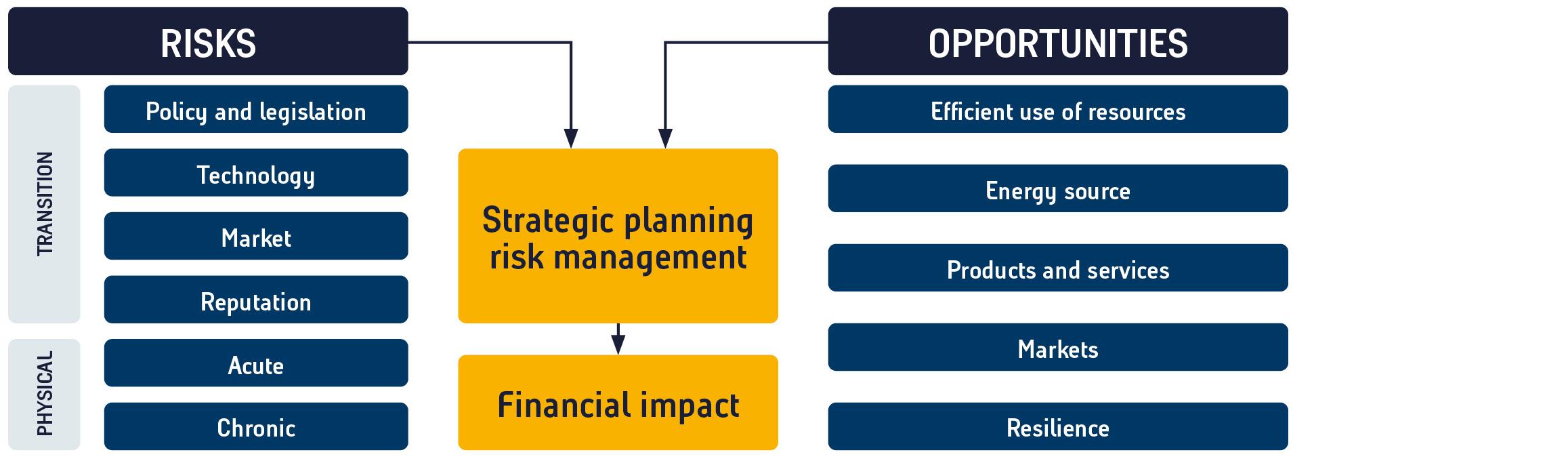
Transition |
Policy and legislation |
1 |
Higher price for GHG emissions |
M |
Will eventually become visible in charging on of purchased products |
|
2 |
Improved emissions reporting obligations |
M |
Heijmans already reports according to standards |
||
|
3 |
Increasing regulation related to limitation of greenhouse gas emissions |
H |
Immediately visible when purchasing new equipment and in additional requirements municipalities in construction projects |
||
|
4 |
Mandates for and regulation of existing products and services |
M |
Part of regular tenders |
||
|
5 |
Exposure to legal cases |
L |
Heijmans is one of the frontrunners, which means risks are lower, management systems and certifications are in place |
||
|
Technology |
6 |
Replacement of existing products and services by lower emission options |
L |
New technologies are already part of our designs |
|
|
7 |
Unsuccessful investments in new technologies |
M |
Heijmans wants to be at the forefront of equipment procurement. Part of investment monitoring. Heijmans is constantly on the look out for more sustainable and smarter materials and solutions |
||
|
8 |
Costs related to switch to lower emission technology |
H |
Emission-free construction demands relatively high investment in new equipment |
||
|
Market |
9 |
Changing behaviour of clients |
L |
Heijmans is able to respond to the changing demand, although not all clients are as far yet |
|
|
10 |
Uncertainty in market signals |
M |
Firm commitment by public sector market, though uncertainty on regulatory front |
||
|
11 |
Increased cost of raw materials |
H |
In particular by passing on CO2 pricing and longer supply routes |
||
|
12 |
Declining availability of raw materials |
M |
Not necessarily related to climate risks |
||
|
Reputation |
13 |
Shifts in consumer preferences |
L |
Heijmans' designs can meet demand |
|
|
14 |
Stigmatisation of the sector |
L |
Many initiatives and appreciation visible |
||
|
15 |
Increased concerns of stakeholders or negative feedback from stakeholders |
L |
Good contact with stakeholders |
||
|
Physical |
Acute |
16 |
Extreme water levels rivers |
M |
Previous situations managed logistically, though possible price risk and higher insurance costs |
|
17 |
Increase in heavy rainfall |
M |
Water damage construction works is still relatively limited, but it does affect the construction process. |
||
|
18 |
Increasing heat waves |
L |
Relevant for employability of employees and continuity of projects, can be managed with measures |
||
|
19 |
Increasing forest fires |
L |
Is more relevant in nature areas than built environment |
||
|
20 |
Increasing high winds and storms |
M |
Damage to construction sites and buildings due to windstorms (usually insurable) |
||
|
Chronic |
21 |
Changes in rainfall patterns and extreme variabiliy in weather patterns |
L |
Mostly long-term measures possible |
|
|
22 |
Rising sea levels |
L |
Permits for construction in certain areas |
||
|
23 |
Rising average temperatures |
L |
Measures possible in design and required in regulation. |
||
|
24 |
Changing ecosystems (including biodiversity) |
L |
No relevant impact on direct operations, is an opportunity for service delivery. Emergence of persistent exotic species |
L = Low risk/opportunity M = Medium risk/opportunity H = High risk/opportunity
|
Type |
# |
Climate-related opportunity |
Relevance to Heijmans |
|
|
Efficient use of resources |
1 |
Use of more efficient transport modes and production and distribution processes |
M |
Focus on industrialisation and sustainable mobility |
|
2 |
Use of recycling |
M |
Great deal of attention in talks with suppliers |
|
|
3 |
Switch to more efficient buildings |
H |
Essential part of new building design and renovation |
|
|
4 |
Reduced water use and consumption |
L |
So far less relevant in Dutch context |
|
|
Energy sources |
5 |
Use of lower emission energy sources |
H |
Application of products and services in the built environment, such as development of electrcity grid and underground infrastructure. |
|
6 |
Use of supporting policy incentives |
M |
Part of business cases, use of subsidies |
|
|
7 |
Use of new technologies |
M |
Standardisation of use of heat pump technologies and alternative services |
|
|
8 |
Participation in CO2 market |
L |
So far no business models that can convert energy savings into carbon credits |
|
|
9 |
Shift towards decentralised energy generation |
H |
Many solutions available for individual homes and clusters of neighbourhoods |
|
|
Products & services |
10 |
Development and/or expansion of low-emission goods and services |
H |
Both in housing and building designs and energy supply. Opportunities due to network expansion (electricity, H2) |
|
11 |
Development of climate adaptation and insurance risk solutions |
H |
In particular, building dykes, modifying sewage systems and water storage in cities. |
|
|
12 |
Development of new products or services through R&D and innovation |
M |
Heijmans' role is more a system integrator and launching client than an innovator |
|
|
13 |
Potential to diversify business activities |
M |
Mostly expansion of existing products and services |
|
|
14 |
Shift in consumer preferences |
H |
Potential to provide clients with sustainable solutions |
|
|
Markets |
15 |
Access to new markets |
H |
Primarily the energy market, development, management and maintenance systems/pipes |
|
16 |
Use of government incentives |
H |
Contribution to investments in sustainable equipment and renewable energy systems, often indirectly (renovation) |
|
|
Resilience |
17 |
Participation in renewable energy programmes and adoption of energy efficiency measures |
H |
Various joint ventures (see also overview Green Deals and collaborations) |
|
18 |
Resource substitution/diversification |
M |
Primarily in the renovation market, switch from gas to electricity |
|
|
19 |
Green financing |
M |
There will be opportunities, but often not a decisive factor in the business case. We will continue to investigate this |